What is Valuation



Valuation is the process of determining the fair market value of an asset. Valuations can be done on assets (for example, investments in marketable securities such as stocks, options, business enterprises, or intangible assets such as patents and trademarks) or on liabilities (e.g., bonds issued by a company). Valuations are needed for many reasons such as investment analysis, capital budgeting, merger and acquisition transactions, financial reporting, taxable events to determine the proper tax liability, and in litigation. Valuation is
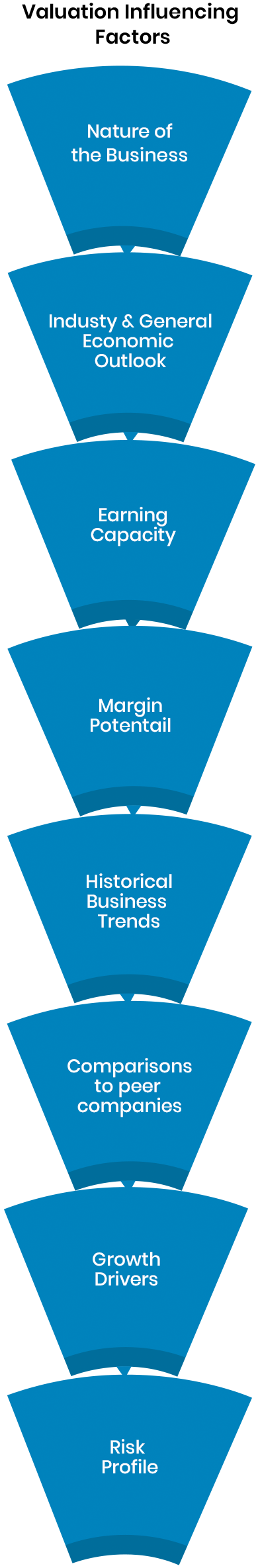
A formal valuation can only be conducted by a qualified valuer who has undertaken prescribed education and training in this field to ensure that they take into account all features and issues relating to a particular property. Valuing is a complex task and will take some time to complete. A formal valuation will take into account things such as
After a valuation, the client will receive a written report detailing the value of the property and a fee will be charged for this service.
Valuations are required when a definitive value is needed. Reasons for this include a property settlement, obtaining finance from a lending institution or establishing the value of a deceased estate. A Court may also order that a valuation be obtained as part of the process of resolving a dispute.
If you do require the best indication of price, engage the services of a qualified valuer so that you can be sure of the true value of your property.